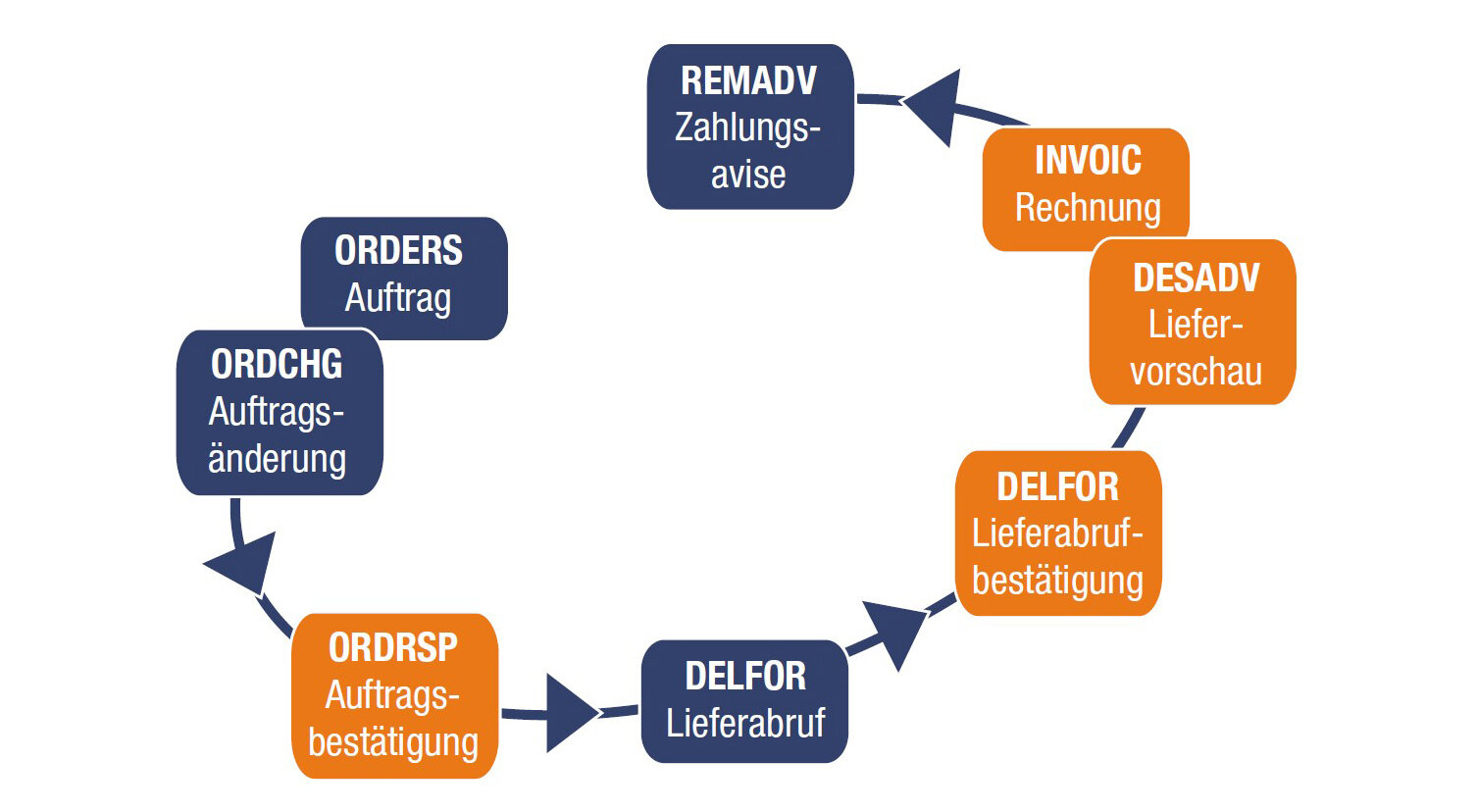
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) refers to the electronic exchange of data between business partners via standardised communication paths (e.g. GXS mailbox) and standardised message formats (e.g. ORDERS = order) which have been defined by relevant organisations (e.g. VDA, UN).
The absence of manual intervention means that the error quota is reduced, the throughput time is cut, all the processing can be fully automated and traceability is improved. Valuable human resources can be deployed elsewhere.
EDI saves time and personnel, makes business processes more transparent and traceable, helps optimise workflows, creates synergies – and can be implemented quickly and easily with standardised technologies.
Automated
Electronic Data Interchange removes the need for manual processes such as recording incoming invoices. Automated processes take less time and need less manpower.
Transparent
Electronic feedback (e.g. order responses), which is made available for the partner-specific enterprise resource planning system (ERP), improves transparency for the various departments. Use of the inhouse IT infrastructure and associated logging ensures that the technical processes can be traced.
Integrated
By using the partner-specific enterprise resource planning system (ERP), employees can make use of their existing knowledge and optimise the workflows. There is no need to use external systems.
Standardised
The use of common internationally accepted standards makes communication easier when implementing and supporting EDI connection.
These properties make EDI a cost-effective way of mapping business processes between business partners.
| Filename | Kind | Size | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| OFTP2 certificate | ZIP File | 9.56 KB | 11.02.2019 |
| https certificate chain production+test system | ZIP File | 9.63 KB | 11.02.2019 |
| http certificate production+test | ZIP File | 9.55 KB | 11.02.2019 |